Surface Settlement Using Electromagnetic Instruments
- Surface Settlement Using Electromagnetic Instruments In The World
- Surface Settlement Using Electromagnetic Instruments Video
Geophysical methods are an important component of geoarchaeological investigations due to their ability to non-invasively image the subsurface of an archaeological landscape . New developments in multi-sensor and positioning technology have facilitated the use of these methods over large areas, allowing archaeological questions to be addressed on a landscape scale. They are particularly useful in geoarchaeological investigations for defining site stratigraphy, mapping site disturbance and reconstructing palaeolandscapes.
Surface Settlement Using Electromagnetic Instruments In The World
Surface Settlement Using Electromagnetic Instruments Video
Geophysical methods also make a significant contribution to archaeological investigations beyond geoarchaeology. Excellent detailed introductions to the application of specific geophysical techniques to archaeology in general are available for ground-penetrating radar (Manataki et al. 2015; Conyers 2013, 2015b), magnetometry (Armstrong and Kalayci 2015; Aspinall et al. 2008), resistivity (Schmidt 2013) and electromagnetic techniques (Simon and Moffat 2015).
1 RULES CONCERNING HANDLING OF SALE AND PURCHASE OF BONDS, ETC. WITH DELAYED SETTLEMENT (July 30 1992) (Purpose) Article 1 The purpose of the Rules concerning Handling of Sale and Purchase of Bonds, etc. With Delayed Settlement (hereinafter referred to as “Rules”) is to prescribe the necessary matters with regard to the conclusion of.
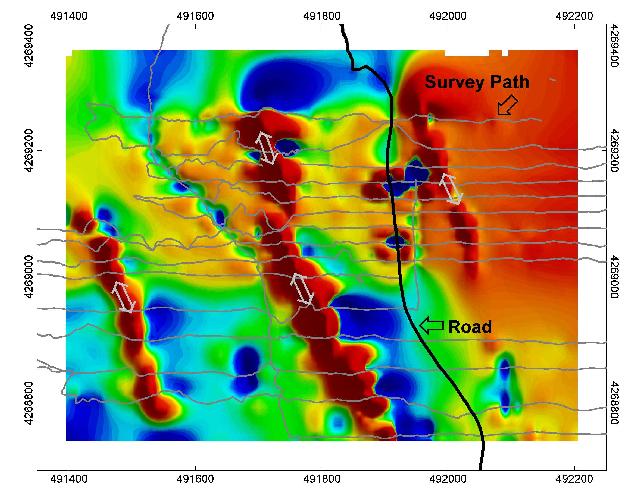
Refers to the natural surface of the earth undisturbed by human activities. It represents vegetation, natural or man-made features and every other visible evidence of land use e.g. Forest, cultivated/uncultivated land, settlement, etc. Land use on the other hand, refers to the use of land by humans. Detection of Resistive Features using Towed Slingram Electromagnetic Induction Instruments Article (PDF Available) in Archaeological Prospection 16(2):103 - 109 April 2009 with 159 Reads.